U.S. beef producers are leaders in sustainability and committed to responsibly raised beef. Here are only a few of the science-backed facts illustrating how U.S. beef producers are sustainability leaders. To learn more, visit beefresearch.org.
1. U.S. vs. Global Emission Intensity
The U.S. beef industry’s emission intensity is two to nine times lower than that of other top beef-producing countries such as Australia, India and Brazil. Since 1996, the U.S. has had the lowest greenhouse gas (GHG) emission intensity in the world.1
2. Cattle: The Ultimate Upcyclers
Every day, cattle graze and turn natural resources like solar energy and pastureland into high-quality proteins and other invaluable products. They’re upcyclers that take otherwise useless materials, add nutritional and environmental value, and transform them into something more.
Approximately 29% of the land in the U.S. is pasture or rangeland that is too wet, rocky, steep or arid to support cultivated agriculture.3 This land can support cattle for protein upcycling.
3. More with Less
U.S. farmers and ranchers produce 19% of the world’s beef, with only 6% of the world’s cattle.4
4. U.S. Improvements in Beef Production
The U.S. beef industry increased the pounds of beef produced per head by 67.58% since 1961 (compared to 2019).5
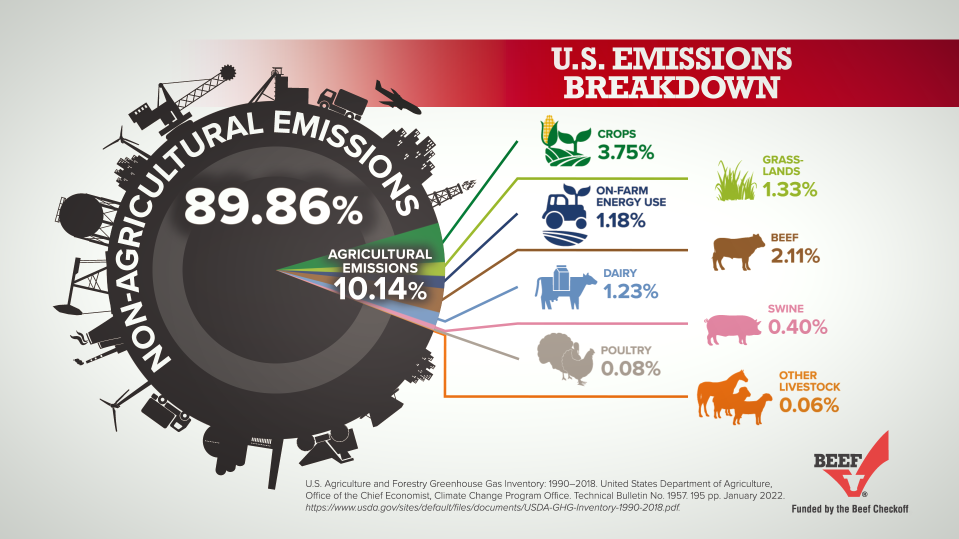
5. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Beef cattle only represented 2.11% of emissions in the U.S. in 2020.6
6. Corn Going to Grain-Finished Beef Cattle
- 6.6% of total corn produced in the U.S. is fed to feedlot cattle.7
- By comparison, 34.8% of corn acreage in the U.S. is used for producing ethanol.8
- Corn acreage used to feed feedlot cattle is 0.2% of total U.S. land area, 1.4% of total U.S. cropland acres and 7% of total U.S. harvested corn acres.9
- The amount of U.S. land used to produce corn to feed grain-finished cattle is less than the size of the Houston Metro area.10
- Climate Watch Data. Agriculture. FAO-STAT. Emissions intensities.
- The emission intensity of the US beef industry is over two times lower than that of Argentina [(Argentina)33.3372/ (US)13.5409 = 2.46x]The emissions intensity of the US beef industry is two times lower than that of Australia. [(Australia) 22.0074/ (US) 13.5409= 1.63x]The emissions intensity of the US beef industry is nearly three times lower than that of Brazil. [(Brazil)39.9941/ (US)13.5409 = 2.95x]The emissions intensity of the US beef industry is nearly two times lower than that of Canada. [(Canada) 14.7452/ (US)13.5409 = 1.09x]The emissions intensity of the US beef industry is over nine times lower than that of India [(India)140.9738/ (US) 13.5409 = 10.41x]
- Climate Watch Data. Agriculture. FAO-STAT. Emissions intensities.
- UN FAOSTAT database. Available at: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home accessed August 17, 2020
- NASS Quick Stats (USDA/NASS QuickStats Ad-hoc Query Tool)
- Found on US EPA 1990-2020 Report: Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2020, updated 04/2022 (epa.gov).
- 7% of total corn produced in the U.S. is fed to feedlot cattle.
- U.S. Bioenergy Statistics 2019/2020
- NASS Quick Stats (USDA/NASS QuickStats Ad-hoc Query Tool)
- USDA ERS. 2021. 2012 ERS Major Uses of Land