Thanks for Asking: Can beef be part of a healthy diet?
March 1, 2024
March 1, 2024
Some people may believe they need to reduce or eliminate beef when focusing on a healthy diet. Not true! Balancing diet and exercise are cornerstones to a healthy lifestyle and consuming lean beef can definitely be a part of a healthy diet.
Here are a few facts and tips to help you incorporate beef into your heart-healthy diet today. Prepare to be surprised. Your taste buds will thank you.
Add Lean & Extra Lean Cuts for a Healthy Diet
Nine extra-lean beef cuts, including extra-lean ground beef, bottom round steak, and top sirloin steak, have the American Heart Association’s Heart-Check certification for foods that fit in an overall heart-healthy dietary program. These cuts have less than 5 grams of total fat, less than 2 grams of saturated fat, and less than 95 mg. of cholesterol per 3.5 oz. serving. For recipes certified by the American Heart Association, visit the Pennsylvania Beef website at www.pabeef.org/healthful-beef-recipes to learn more.

Beef Contains Healthy Fats
Monounsaturated fatty acids, the same type of healthy fat found in avocados and olive oil, are also found in beef.1,2 Roughly half of the fatty acids in beef are considered monounsaturated.
Beef contains stearic acid, the same fat recognized as beneficial in chocolate for its neutral effect on blood cholesterol levels.1,3,4,5 About one-third of beef’s saturated fat is stearic acid.
Beef Protein Plays Role in Weight Management
A 3-oz. serving of cooked beef provides about 50 percent of the Daily Value (25 grams) of protein. In short, beef helps with weight management by:
Lean Beef is Part of the Mediterranean Diet
The ever-popular Mediterranean diet includes lean beef in addition to fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts/seeds and olive oil. In fact, did you know that the intake of red meat in many Mediterranean countries is similar to that of the United States and, in some countries, even more?1 Research shows a Mediterranean-style diet that includes lean, unprocessed red meat supports heart health and is effective at improving certain heart disease risk factors (like blood pressure, total cholesterol, and LDL cholesterol).12
Beef + Fruit = A Great Partnership
Which do you prefer – sweet or savory? How about combining the two? Consider pairing beef with fruit to find a beautiful blend of taste and nutrition. Try making a beef tenderloin, cranberry, and pear salad for dinner tonight. Then again, perhaps citrus kabobs are more your style. These recipes and more are found on the Pennsylvania Beef website at www.pabeef.org/recipes-cooking.

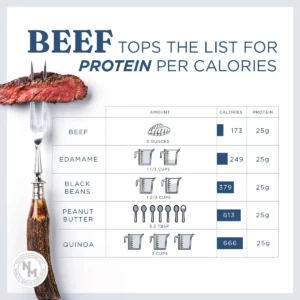
Beef Packs a Protein Punch
A 3-oz. serving of cooked beef provides more than 10 essential nutrients and about half the Daily Value for protein in about 175 calories.13 These essential nutrients include:
Regarding high-quality proteins, beef provides many nutrients in a smaller serving size than other choices. For example, you’d have to eat at least 8 oz. of cooked chicken breast to get the same amount of iron in just 3 oz. of cooked beef.13
Grass-Finished or Grain-Finished Beef? Both Work in a Healthy Diet
Grass-finished and grain-finished beef provide similar nutritional benefits. Whether grass- or grain-finished, all cattle spend most of their lives eating grass. Although grass-finished beef may be a bit leaner, all beef is still a natural source of more than 10 essential nutrients.14
Sources